Landline:+86-0775-84649797 Phone:+86 19926651112(Same WeChat ID)
Share:
RFID in the Olympics: Technology for event management
In the 21st century, rapid technological advancements have permeated every aspect of our lives, and sports events are no exception. As one of the world's largest sporting spectacles, the Olympic Games serve as not only a platform for athletes to showcase their skills but also as a testing ground for technological innovation. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has seen increasing applications in various aspects of the Olympics, given its efficiency, accuracy, and security. RFID has played a crucial role in athlete management, event security, and spectator services. In the Olympic Games, RFID has become an indispensable key technology for enhancing the spectator experience.
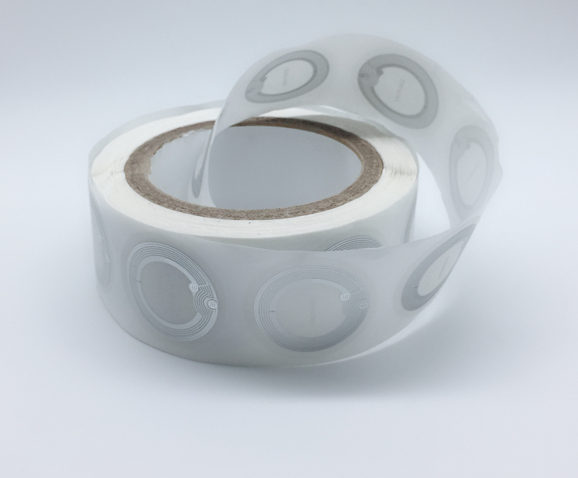
RFID Products in the Olympics:
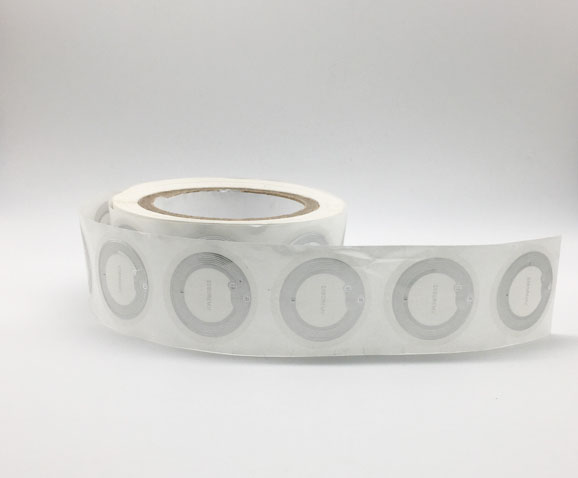
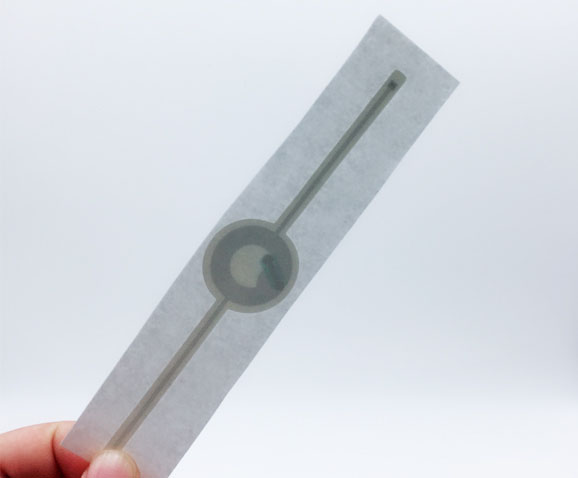
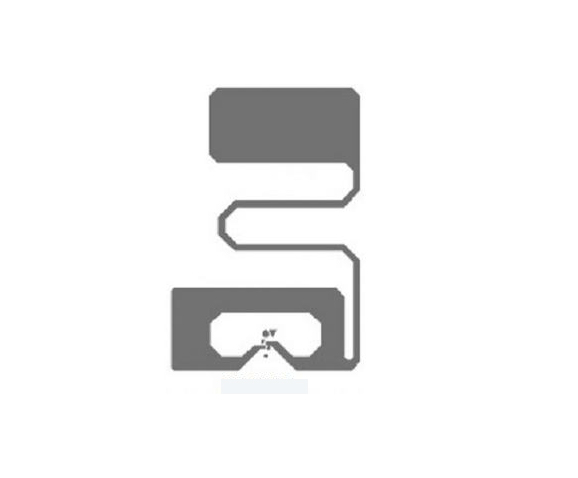
RFID wristbands are convenient and user-friendly RFID products typically made of flexible materials. They can be comfortably worn on the wrist, and with the embedded RFID chip, they can store data such as athlete identification and event information. In the Olympics, athletes and staff can wear RFID wristbands to communicate with readers through the embedded chips, enabling functions such as identity recognition and access control. This provides accurate data to organizers, assisting in better management and organization of the events. Additionally, RFID wristbands can be integrated with other systems, enabling various applications such as payment functions and access control, providing more convenient services to participants in the Olympics.

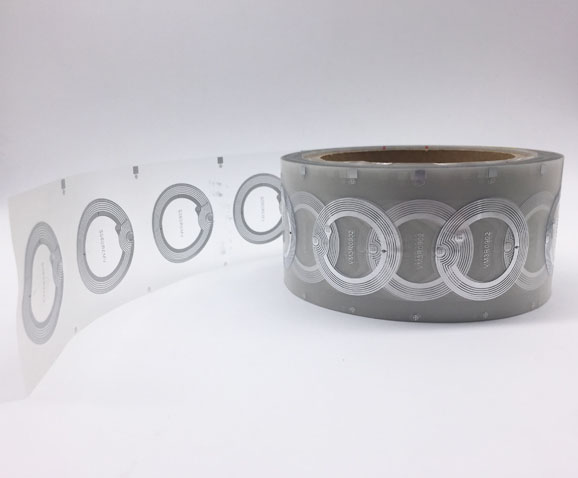
Bluetooth positioning cards are positioning devices based on Bluetooth technology. They communicate with surrounding Bluetooth signals to track and locate targets. During the Olympics, a large number of security personnel need to patrol and monitor different venues. Bluetooth positioning cards can help security personnel accurately track and locate their positions, promptly responding to emergencies and ensuring the safety of the events. Additionally, Bluetooth positioning cards are widely used for real-time positioning of athletes and staff within Olympic venues, accurately recording their locations and activity trajectories, providing valuable data support for event management. Moreover, Bluetooth positioning cards can be combined with other smart devices to achieve functions such as navigation guidance and emergency rescue, enhancing venue security and management efficiency.
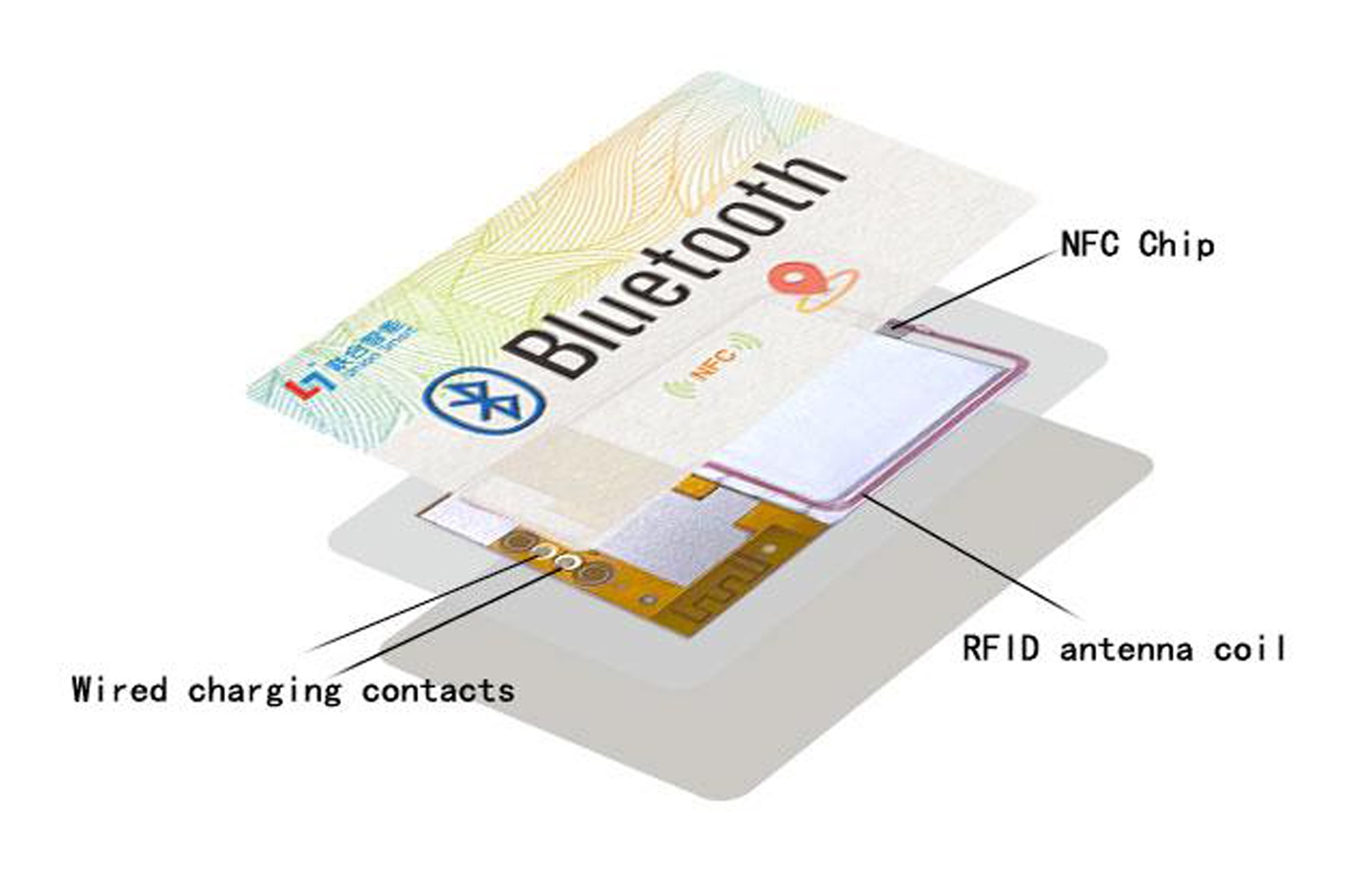
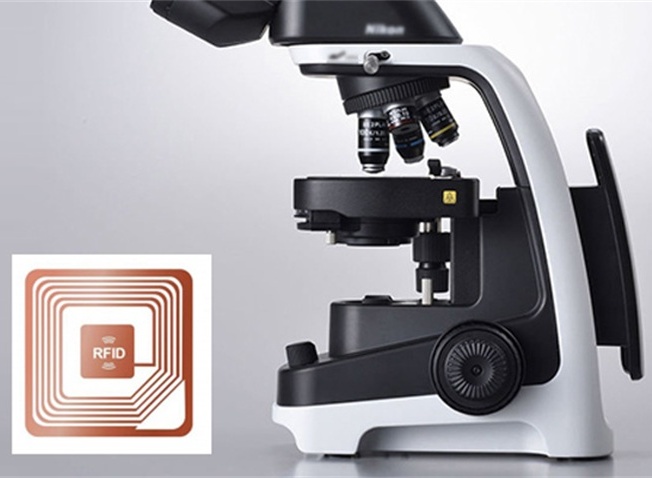
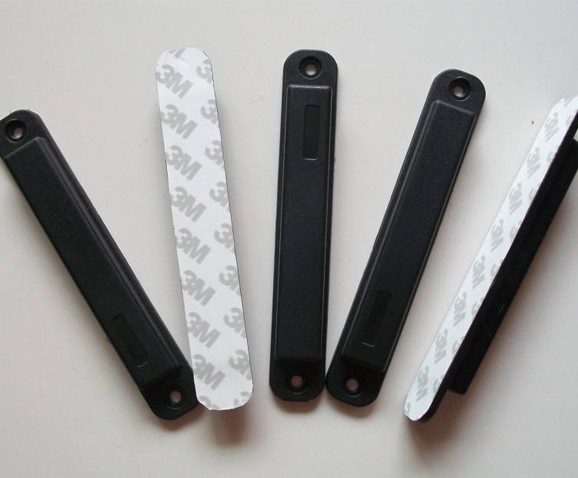
Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) technology, based on ultra-wideband pulse signals, is a wireless communication technology known for its high-precision positioning and strong anti-interference capabilities. In Olympic track and field events, UWB technology enables high-precision positioning and distance measurement. Athletes wear clothing equipped with UWB tags, which accurately measure and record their performance and start times. This provides referees with precise data, ensuring fair and accurate results. UWB tags can also be used to identify and track sports equipment, track facilities, and other items, monitoring their locations and status in real-time, ensuring the supply and safe management of resources during the events.
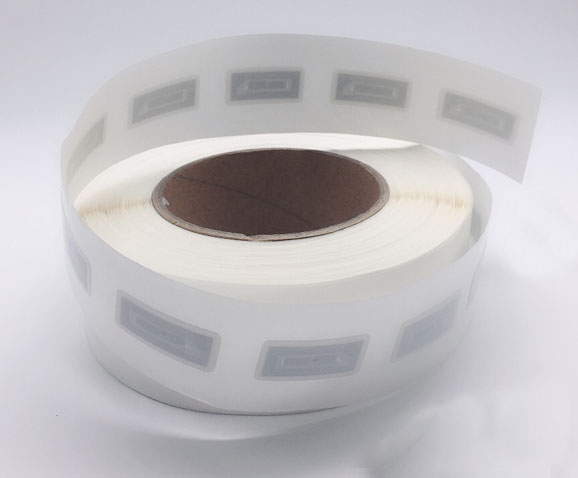
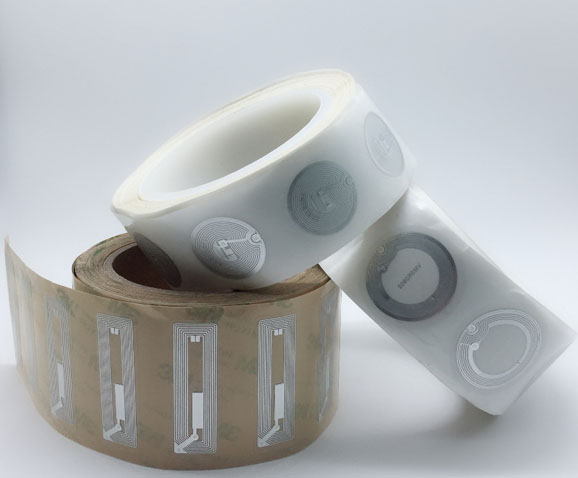
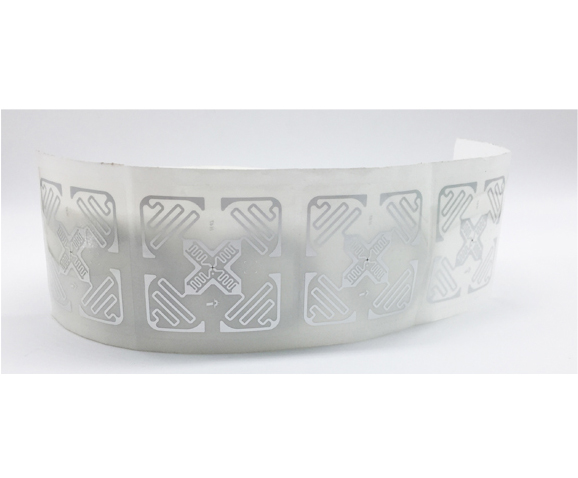
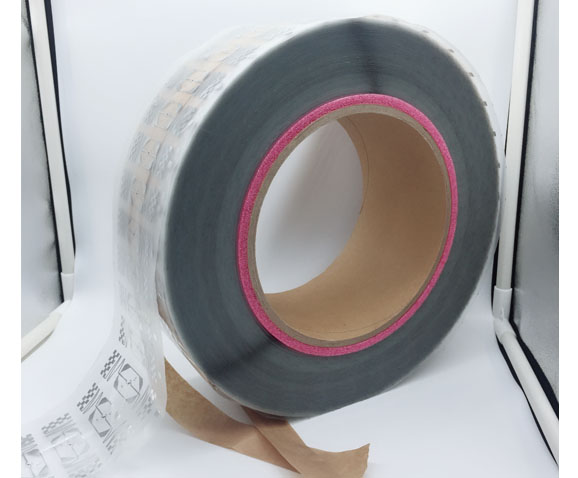
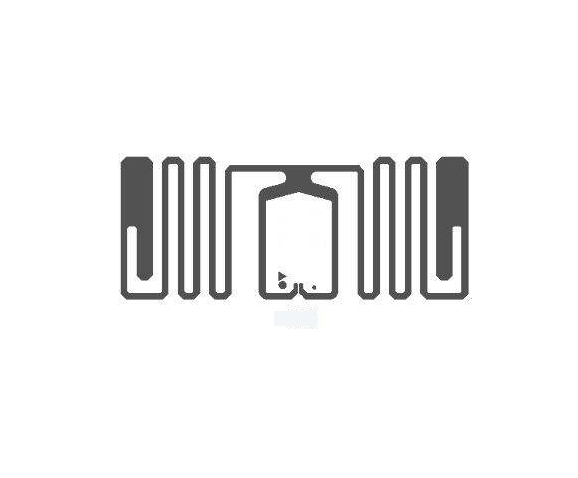
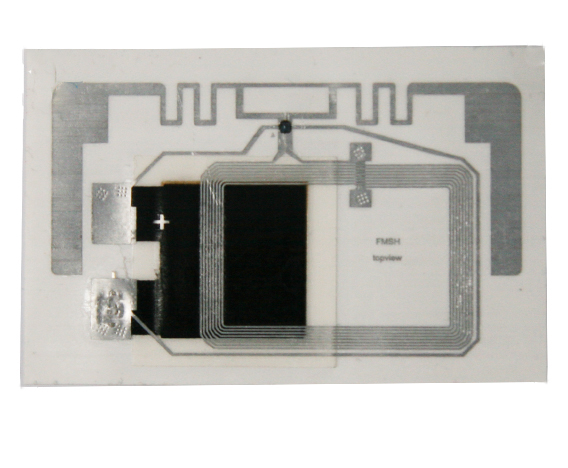
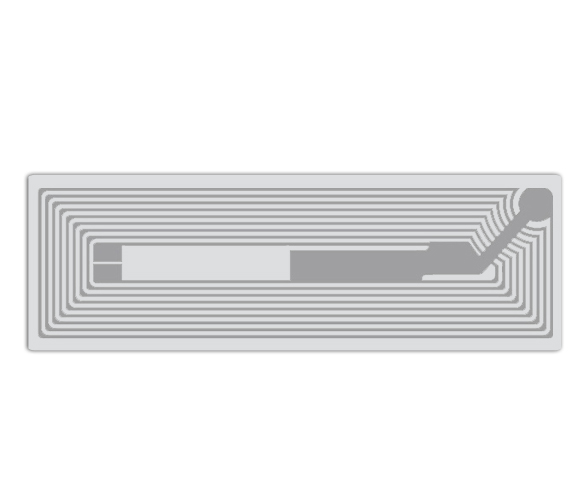
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) tags are RFID products widely used in logistics, warehousing, and other fields. They have characteristics such as long reading distance and fast reading speed. In the Olympics, UHF tags are commonly used to identify and manage large equipment, vehicles, and other resources, enabling quick and accurate recognition of their information, ensuring the supply and safe management of resources during the events. Compared to other RFID products, UHF tags are advantageous when it comes to large-scale resource management, with relatively lower costs. UHF tags can also be tied to spectators' tickets, facilitating fast entry and exit management. By simply bringing the UHF tags on their tickets close to the card reader, spectators can quickly pass through entrance gates without waiting in queues. This not only improves the efficiency of spectator entry but also reduces the workload of manual queue management, enhancing the overall service level of the events.
With ongoing technological advancements and expanding application scenarios, we believe that RFID technology will achieve even wider applications and development in the future. Firstly, as technology continues to progress, the performance of RFID products will further improve, offering greater reading distances, faster data transmission rates, and playing increasingly important roles in large-scale events such as the Olympics. Secondly, RFID technology will merge with other advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, promoting the intelligent and digital development of sports events. For example, combining RFID technology with artificial intelligence can enable real-time monitoring and analysis of athletes' training status, providing personalized training recommendations to coaches, thus improving athletes' competitive performance. We look forward to seeing RFID technology being more widely applied in other domains, making greater contributions to societal development and progress.
RFID Products in the Olympics:
RFID wristbands are convenient and user-friendly RFID products typically made of flexible materials. They can be comfortably worn on the wrist, and with the embedded RFID chip, they can store data such as athlete identification and event information. In the Olympics, athletes and staff can wear RFID wristbands to communicate with readers through the embedded chips, enabling functions such as identity recognition and access control. This provides accurate data to organizers, assisting in better management and organization of the events. Additionally, RFID wristbands can be integrated with other systems, enabling various applications such as payment functions and access control, providing more convenient services to participants in the Olympics.

Bluetooth positioning cards are positioning devices based on Bluetooth technology. They communicate with surrounding Bluetooth signals to track and locate targets. During the Olympics, a large number of security personnel need to patrol and monitor different venues. Bluetooth positioning cards can help security personnel accurately track and locate their positions, promptly responding to emergencies and ensuring the safety of the events. Additionally, Bluetooth positioning cards are widely used for real-time positioning of athletes and staff within Olympic venues, accurately recording their locations and activity trajectories, providing valuable data support for event management. Moreover, Bluetooth positioning cards can be combined with other smart devices to achieve functions such as navigation guidance and emergency rescue, enhancing venue security and management efficiency.

Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) technology, based on ultra-wideband pulse signals, is a wireless communication technology known for its high-precision positioning and strong anti-interference capabilities. In Olympic track and field events, UWB technology enables high-precision positioning and distance measurement. Athletes wear clothing equipped with UWB tags, which accurately measure and record their performance and start times. This provides referees with precise data, ensuring fair and accurate results. UWB tags can also be used to identify and track sports equipment, track facilities, and other items, monitoring their locations and status in real-time, ensuring the supply and safe management of resources during the events.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) tags are RFID products widely used in logistics, warehousing, and other fields. They have characteristics such as long reading distance and fast reading speed. In the Olympics, UHF tags are commonly used to identify and manage large equipment, vehicles, and other resources, enabling quick and accurate recognition of their information, ensuring the supply and safe management of resources during the events. Compared to other RFID products, UHF tags are advantageous when it comes to large-scale resource management, with relatively lower costs. UHF tags can also be tied to spectators' tickets, facilitating fast entry and exit management. By simply bringing the UHF tags on their tickets close to the card reader, spectators can quickly pass through entrance gates without waiting in queues. This not only improves the efficiency of spectator entry but also reduces the workload of manual queue management, enhancing the overall service level of the events.
With ongoing technological advancements and expanding application scenarios, we believe that RFID technology will achieve even wider applications and development in the future. Firstly, as technology continues to progress, the performance of RFID products will further improve, offering greater reading distances, faster data transmission rates, and playing increasingly important roles in large-scale events such as the Olympics. Secondly, RFID technology will merge with other advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, promoting the intelligent and digital development of sports events. For example, combining RFID technology with artificial intelligence can enable real-time monitoring and analysis of athletes' training status, providing personalized training recommendations to coaches, thus improving athletes' competitive performance. We look forward to seeing RFID technology being more widely applied in other domains, making greater contributions to societal development and progress.
Inquiry