Landline:+86-0775-84649797 Phone:+86 19926651112(Same WeChat ID)
Share:

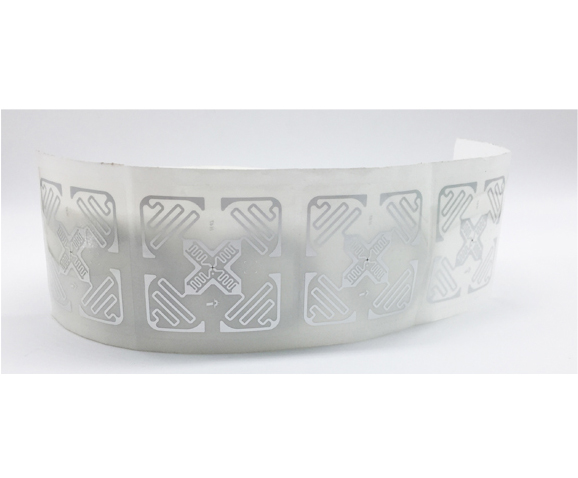
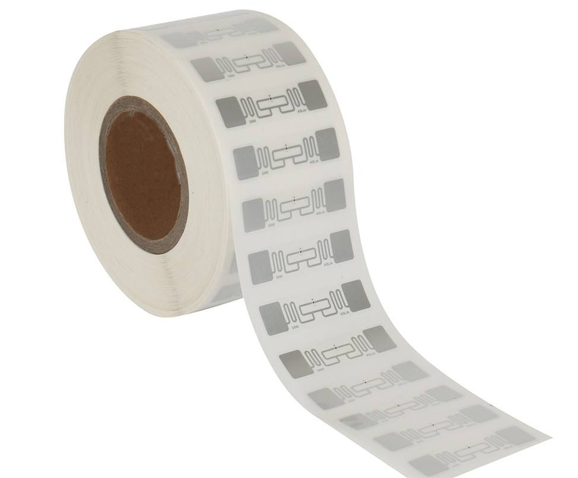
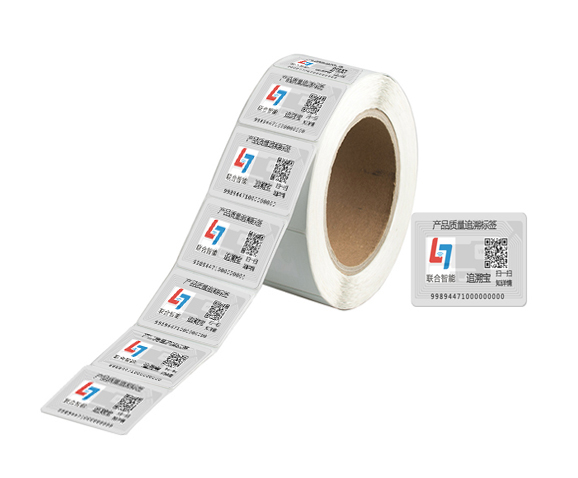
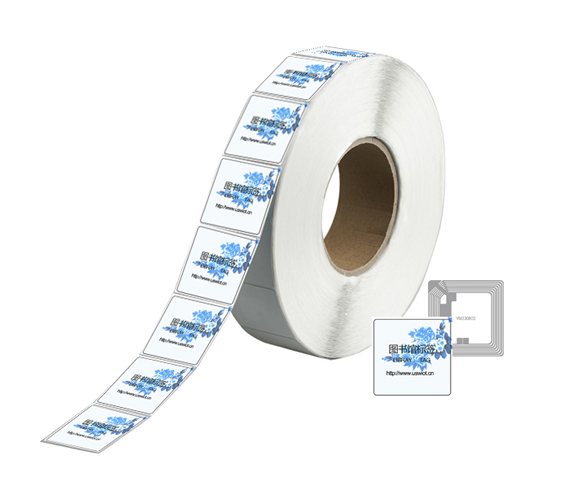
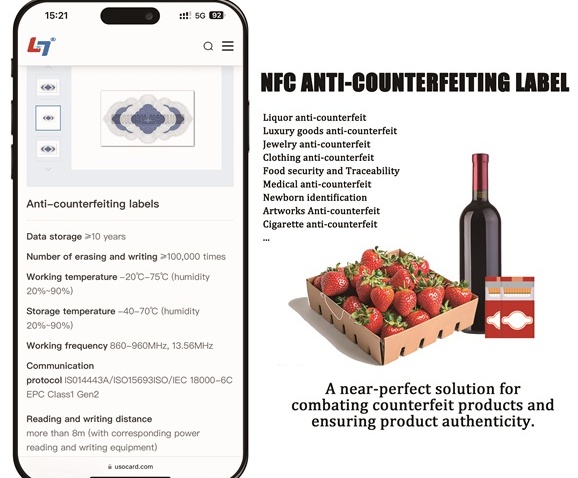
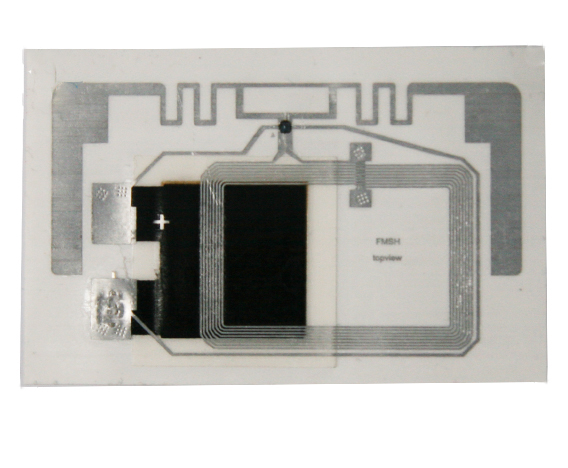
NFC is a short-range and high-frequency wireless communication technology that allows non-contact point-to-point data transmission (within 10cm) to exchange data between electronic devices. Data can be exchanged between different electronic products with a single touch. NFC electronic tag is a wireless connection technology that provides easy, secure and rapid communication. Its transmission range is smaller than that of RFID. The transmission range of RFID can reach several meters or even 10m, because NFC adopts unique signal attenuate technology, NFC has the characteristics of close distance, high bandwidth and low energy consumption compared with RFID.

4 types of NFC electronic tags:
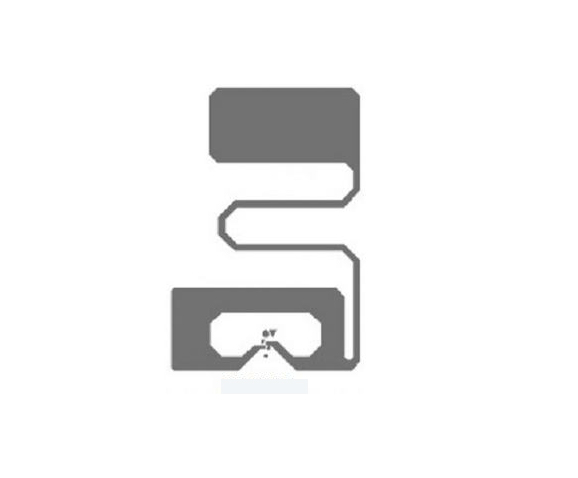
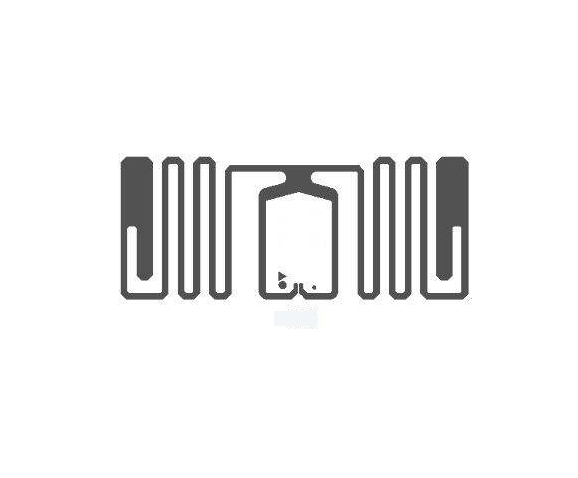
Tag 1 Type -- This type is based on the ISO14443A standard. Such tags have the ability to be read and rewritten, and users can configure them to be read-only. The storage capacity is 96 bytes, which is used to store URL URLs or other small amounts of data. However, the memory can be expanded to 2k bytes. The communication speed of such NFC tags is 106 Kbit/s. These tags are simple and therefore cost effective and suitable for many NFC applications.
Tag 2 Type-- These tags are also based on ISO14443A and are readable and re-writable, which users can configure as read-only. Its basic memory size is 48 bytes, but can be expanded to 2k bytes. Communication speed is also 106 Kbit/s.

Tag 3 Type-- These tags are based on the Sony FeliCa system. Currently has a memory capacity of 2k bytes and a data communication speed of 212 Kbit/s. Therefore, such tags are more suitable for more complex applications, albeit at a higher cost.
Tag 4 Type-- Such tags are defined to be compatible with the ISO 14443A, B standard. The manufacturing time is preset to be readable/rewritable or read-only. Memory capacity up to 32k bytes, communication speed between 106 Kbit/s and 424 Kbit/s.

Comparison of NFC electronic label and RFID label:
1. Security: Compared with traditional electronic tags, NFC electronic tags have irreversible encryption algorithms, close communication distance, high bandwidth, low power consumption, and are very useful for industries with high security requirements such as payment.
2. Can be interactive: NFC electronic tags integrate card readers, antennas, chips, and can interact with close-range messages.

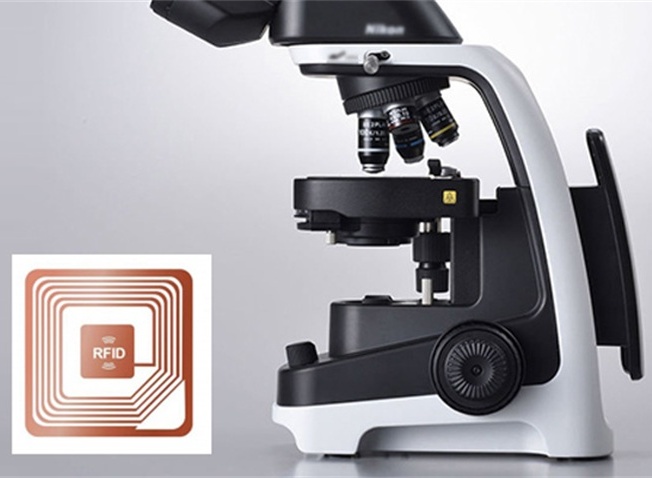
NFC electronic tag application areas: access control attendance, membership management, mobile payment, tickets, subway, public transport, storage information, etc.
Given the efficiency and convenience of NFC technology, NFC users can enjoy the convenience of wireless payment by simply swiping the NFC phone. In the future, NFC will play a huge role in the fields of access control, public transportation, and mobile payment.
Inquiry